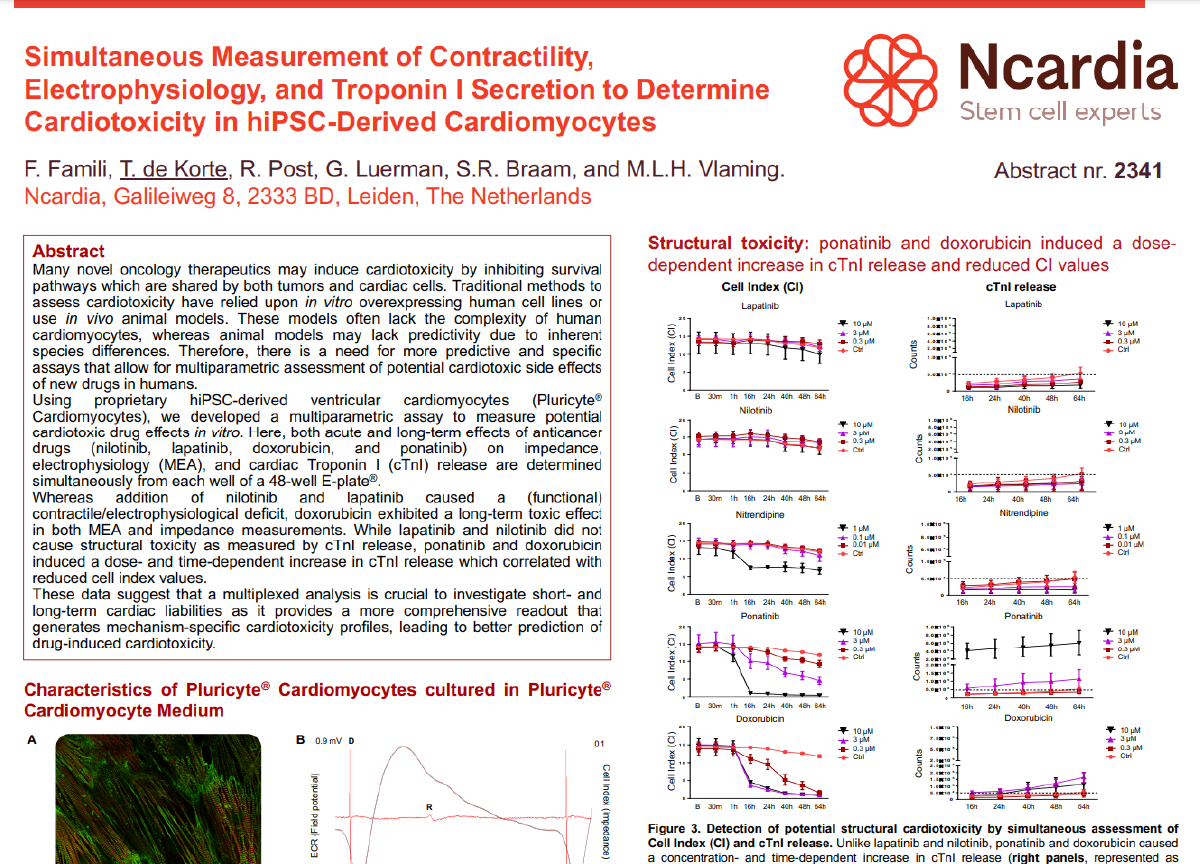
Electrophysiology
Multi-Electrode Array
(MEA) Analysis
Alterations in the electrical activity of neuronal and cardiac cells are associated with severe diseases like epilepsy or cardiac arrhythmias. Multi-electrode array (MEA) uses microelectrodes embedded in the surface of multi-well cell culture plates to provide detailed information about the electrophysiological function of healthy or diseased cells without disturbing cell membrane or adding voltage-dependent dyes.
Combining our expertise in human iPSC technology and the best-in-class Maestro MEA assay you can study the influence of any therapeutic on the electrical function of clinically relevant models.
- Multiple and longitudinal real-time recordings
- Multiplexing options
- Broad throughput screening range
Do you want to explore how this assay can help you progress your drug discovery programs?
Applications
MEA analysis can be used to investigate the electrical activity of human iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes and their acute and chronic responses to drugs. This allows for determining drug efficacy for the treatment of arrhythmias, or for studying your compounds’ cardiac safety profile as part of the Comprehensive in vitro Proarrhythmia Assay (CiPA) initiative.
MEA analysis on iPSC-derived neuronal models can be used to analyze physiologically relevant patterns of neuronal firing that recapitulate normal or diseased brain activity, enabling phenotype-rescue studies for efficacy testing.
MEA recordings of Ncardia’s iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes to study the effects of known ion channel blockers and cardiotoxic compounds.
Most cardiac side effects, like torsade de pointes and ventricular fibrillation, are associated with drugs interfering with the function of ion channels. With a relevant in vitro model and MEA analysis, we can capture drug-induced changes in different ion channels to determine drug safety and cardiotoxicity.
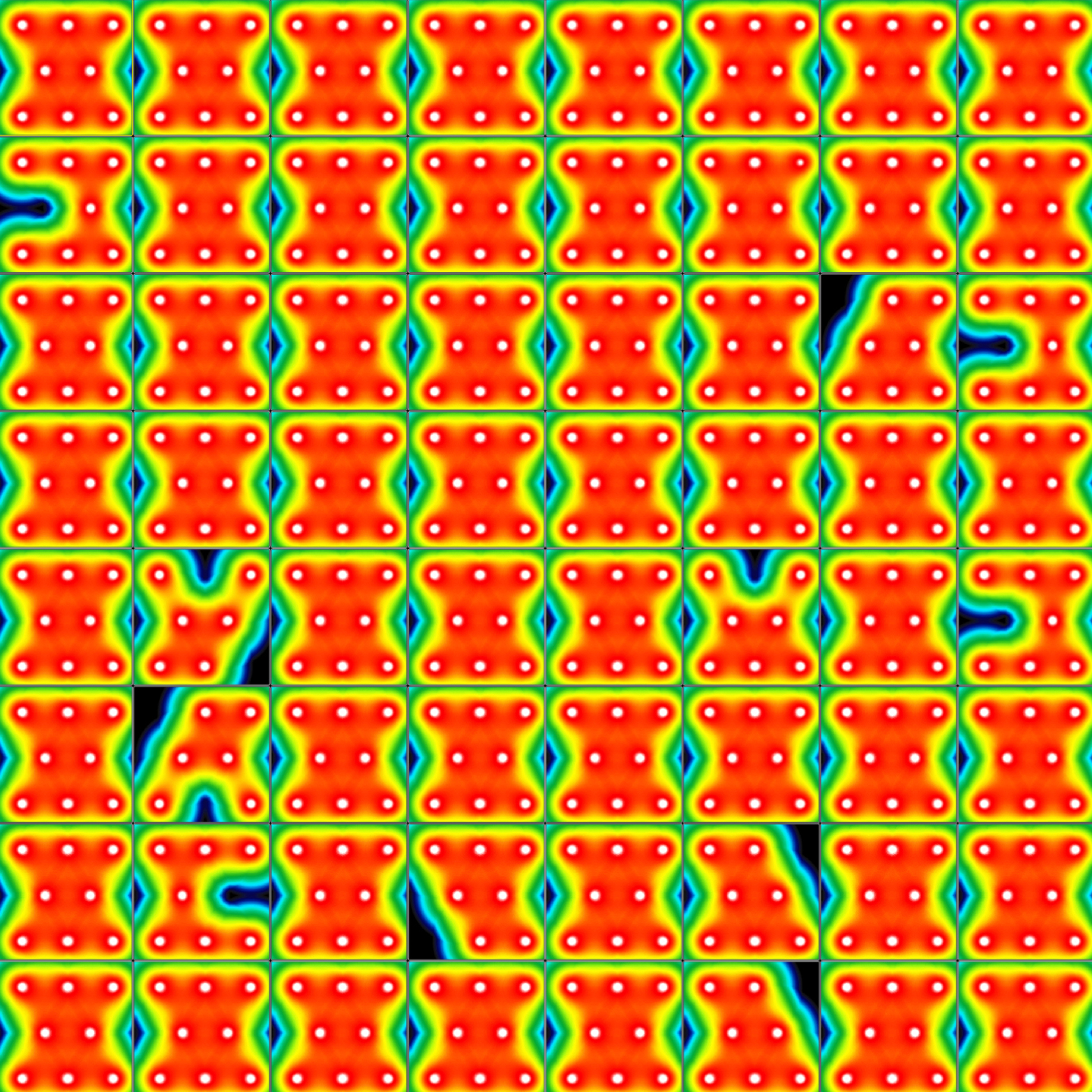
 Nifedipine, an L-type calcium channel blocker, shortened the field potential duration (FPD) of Ncyte Cardiomyocytes in a dose-dependent manner
Nifedipine, an L-type calcium channel blocker, shortened the field potential duration (FPD) of Ncyte Cardiomyocytes in a dose-dependent manner
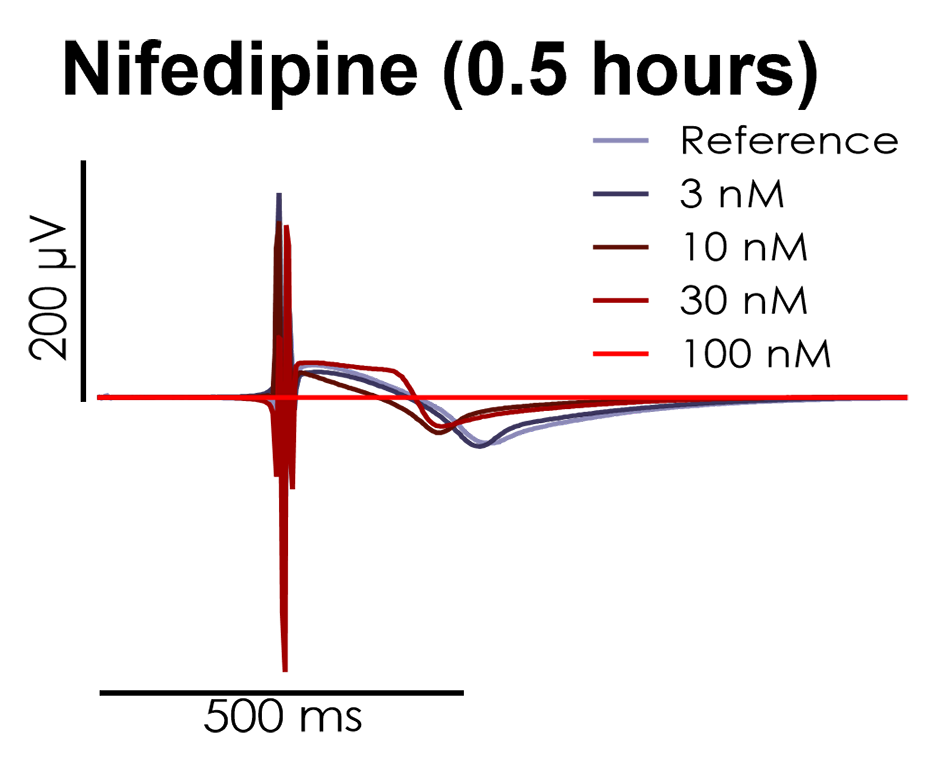
 Nifedipine, an L-type calcium channel blocker, shortened the field potential duration (FPD) of Ncyte Cardiomyocytes in a dose-dependent manner
Nifedipine, an L-type calcium channel blocker, shortened the field potential duration (FPD) of Ncyte Cardiomyocytes in a dose-dependent manner
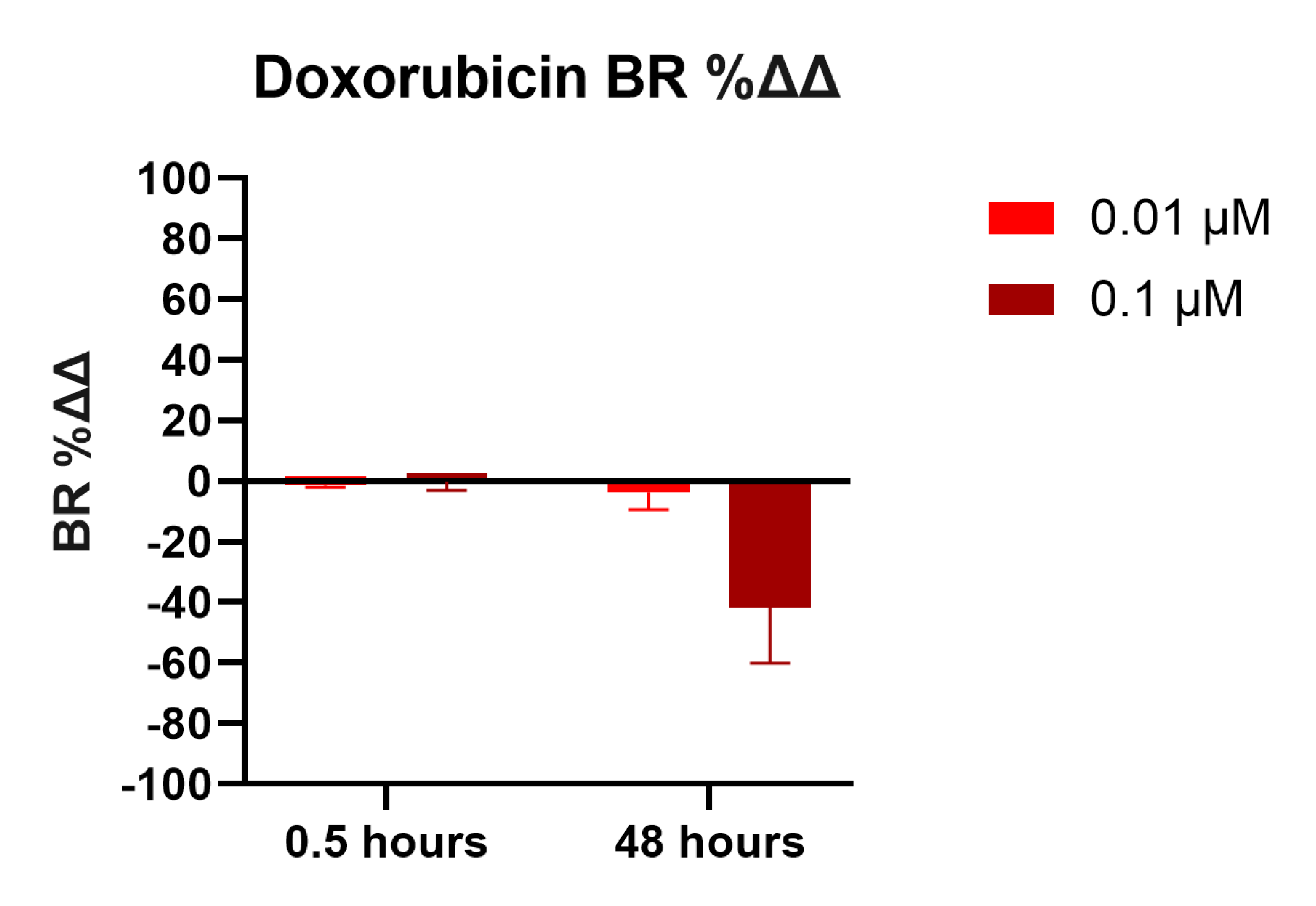 Doxorubicin, a cardiotoxic compound, induced a dose-dependent decrease in beat rate in Ncyte Cardiomyocytes 48h after treatment. This is a deleterious effect for cardiac function.
Doxorubicin, a cardiotoxic compound, induced a dose-dependent decrease in beat rate in Ncyte Cardiomyocytes 48h after treatment. This is a deleterious effect for cardiac function.
MEA recordings of Ncyte CNS neurons to assess drug-induced seizure-liability on network burst.
Epilepsy is characterized by abnormal brain activity that can be replicated in vitro with human iPSC-derived neurons and MEA. Treatment with carbachol (cholinergic agonist) or 4-Aminopyridine (Kv blocker), enable development of seizure assays as disease models for epilepsy and assessment of anti-epileptic drug efficacy.
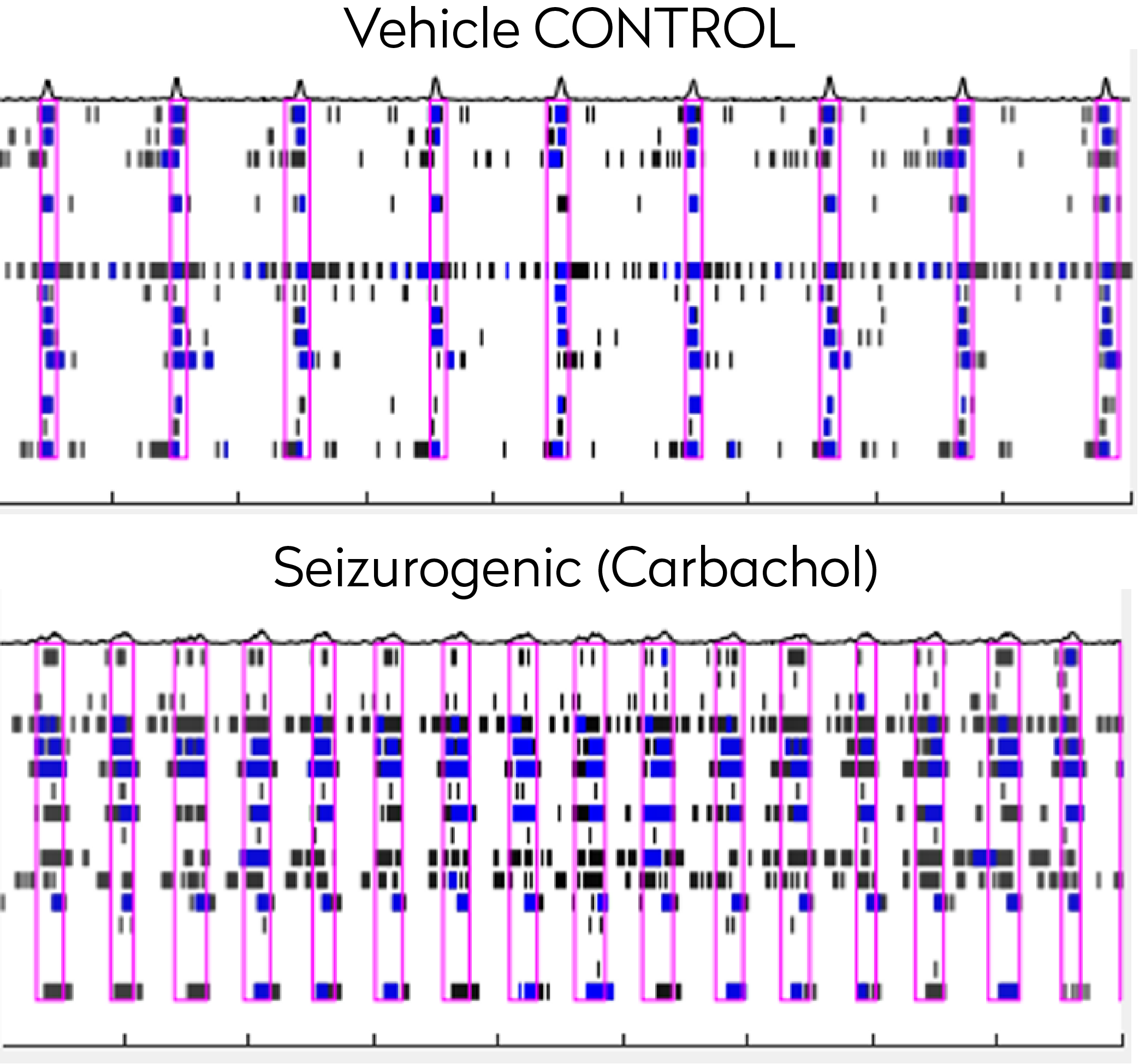 MEA recording of control and human iPSC-derived neuronal firing after treatment with carbachol 20uM (Muscarinic R agonist)
MEA recording of control and human iPSC-derived neuronal firing after treatment with carbachol 20uM (Muscarinic R agonist)
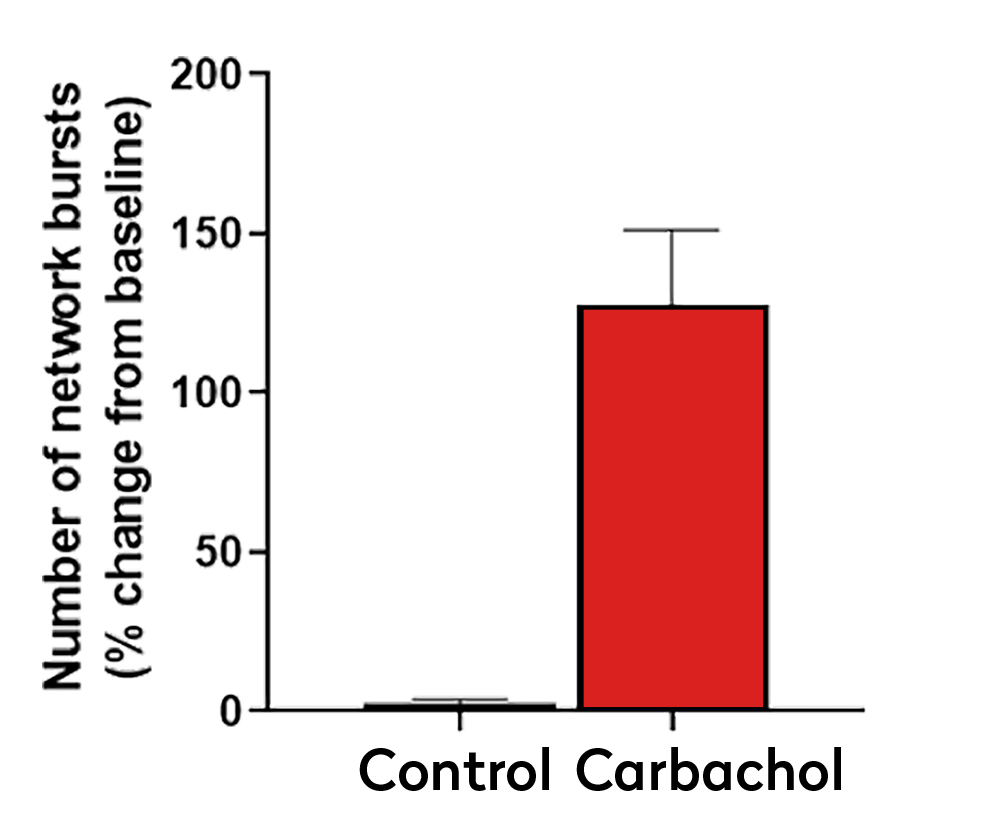 Graph showing the increased in the number of network bursts after treatment with carbachol.
Graph showing the increased in the number of network bursts after treatment with carbachol.
Our work centers on a simple yet powerful premise:
When we combine deep iPSC knowledge, broad assay capabilities and a demonstrated ability to integrate the biology of human diseases into preclinical research, we can help drug developers make critical decisions earlier and with more confidence.
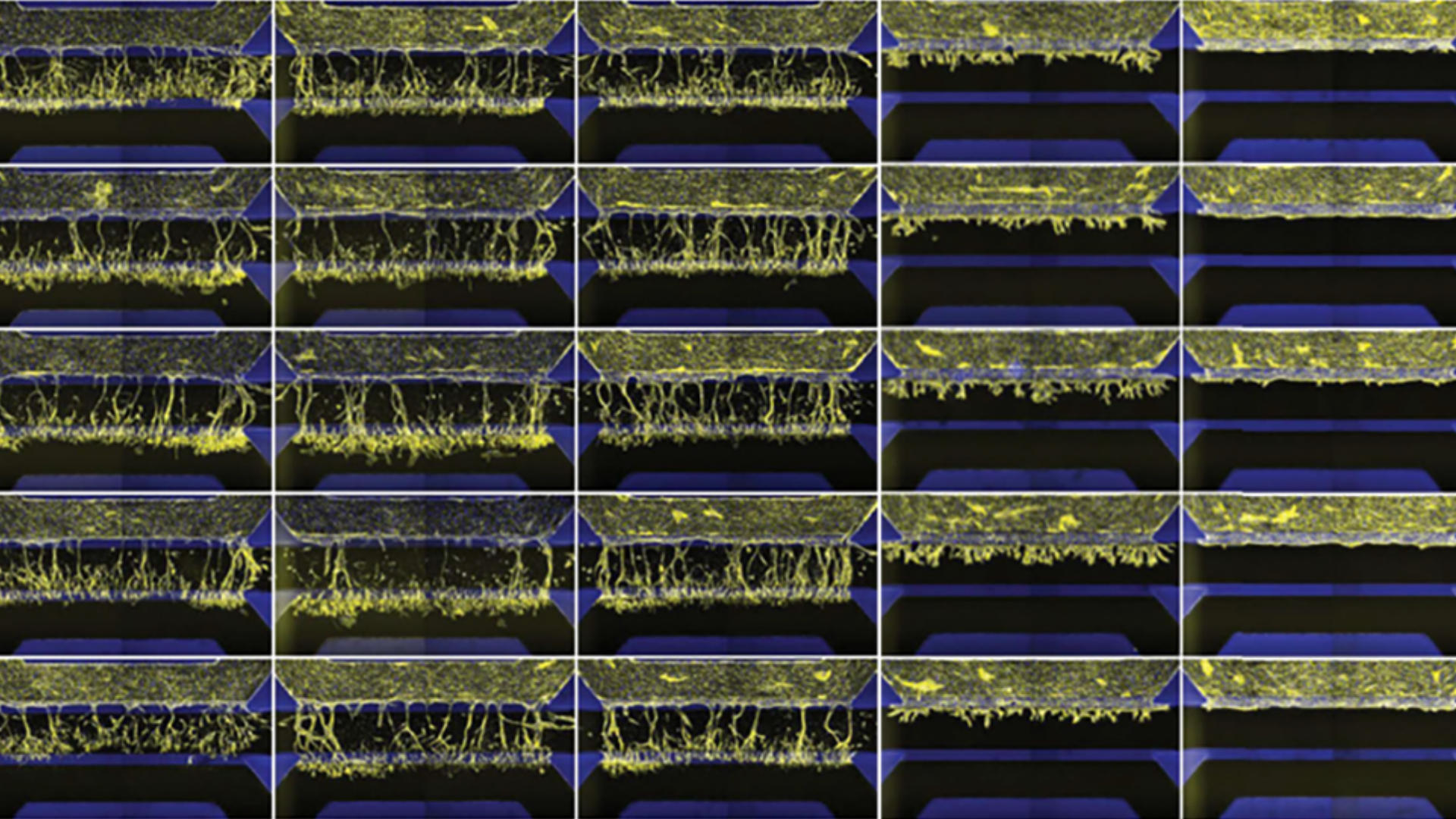
Study compound-induced effects on blood vessel formation
Assay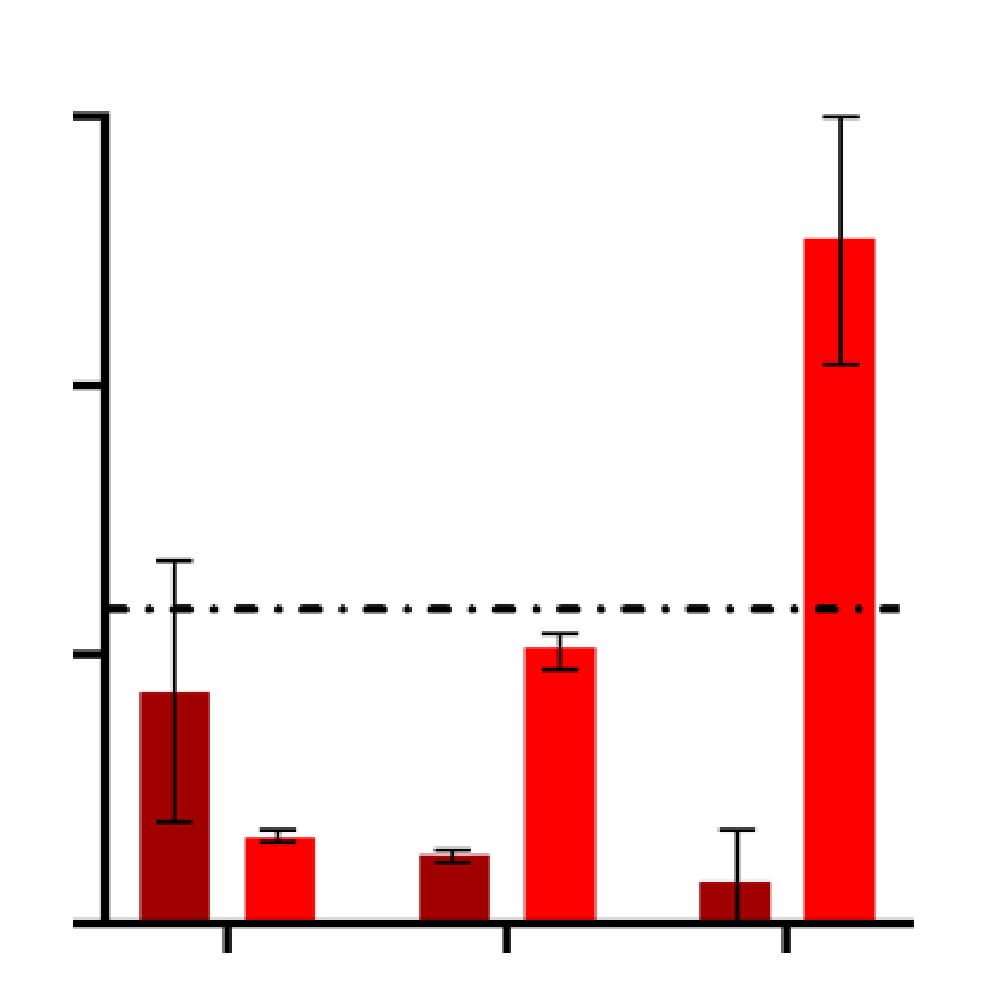
Evaluate and quantify the levels of clinically relevant biomarkers
Assay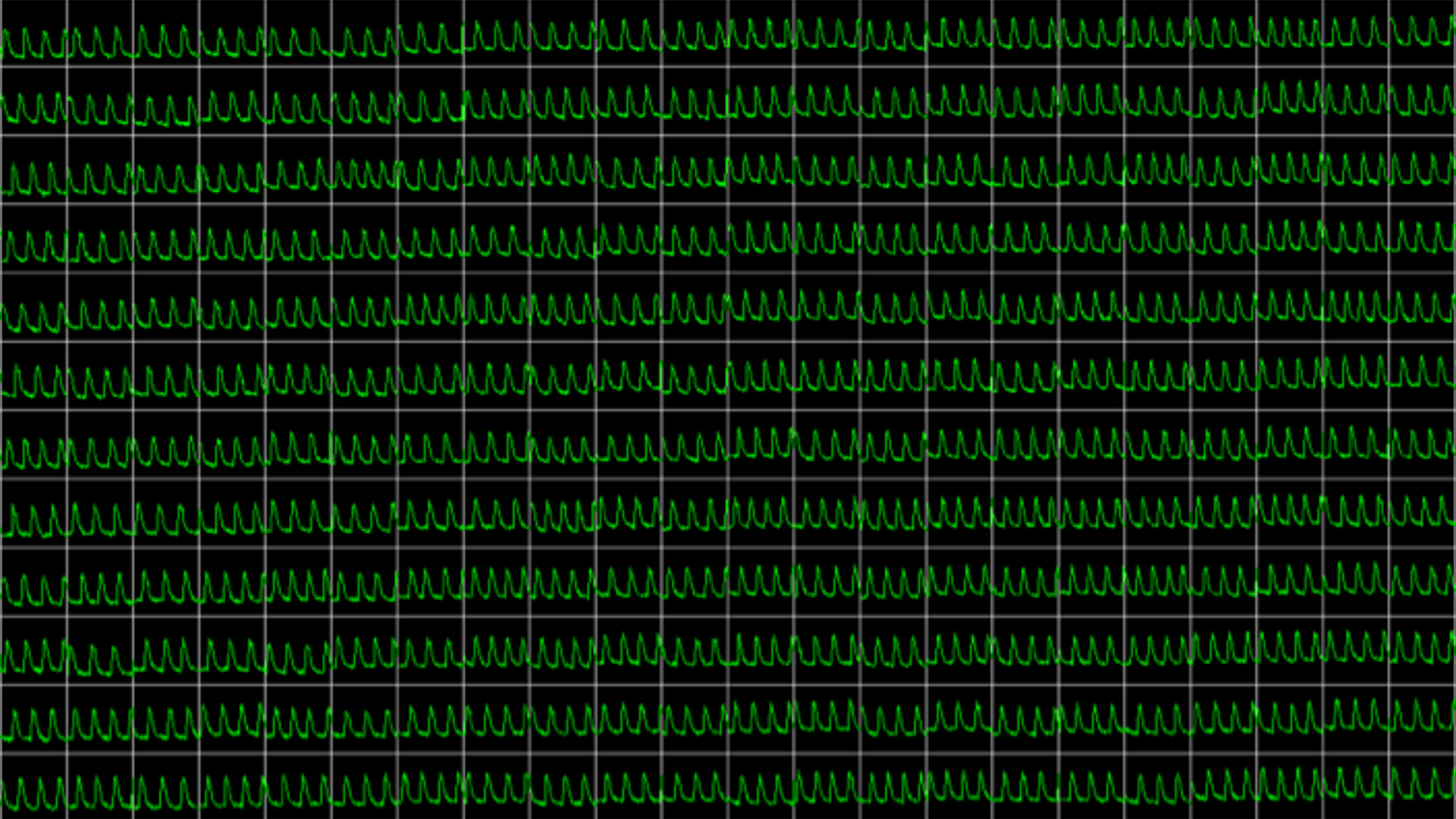
Obtain real-time recordings of intracellular calcium fluctuations
Assay
Get in-depth and unbiased insights into the effects of therapeutic candidates on cells
Assay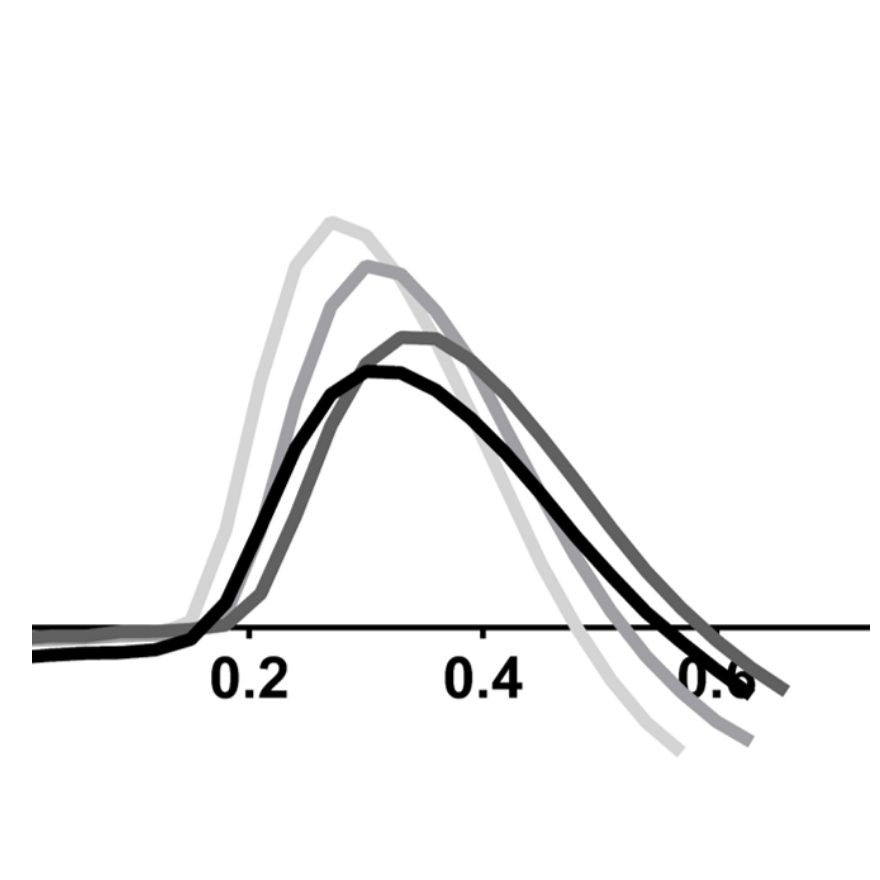
Study drug-induced effects on contractility of cardiac or skeletal muscle cells
Assay
Determine the electrophysiological effects of your therapeutic candidates
Assay
Evaluate endothelial permeability in short and long term
Assay
Study drug-induced phenotypic changes in the cell model of your interest
Assay
Assess functional toxicity across multiple human iPSC-derived tissues in a single integrated workflow to support safer IO development decisions.
Assay
Obtain precise information on compounds' impact on metabolic processes